Anatomy Of Chest Wall
Anatomy Of Chest Wall. Ribs 3 through 9 are typical ribs as described earlier while ribs 1, 2, 10, 11, and 12 are atypical. 2 left anterolateral thoracotomy through bed of fifth rib. Clinical anatomy students learn to use imaginary lines and bony landmarks on the front and back of the thorax to describe locations of the anatomical structures. The chest wall, like other regional anatomy, is a remarkable fusion of form and function. A complete review of the left lateral chest.
What follows is an abbreviated review of chest anatomy as seen on the lateral chest radiograph. The epidermis is the outermost layer that provides a protective, waterproof seal over the body. Surface features & palpable landmarks o… 1. Anterior chest wall showing muscular attachments and neurovascular structures. Learn about each muscle, their locations & functional anatomy.

Principal functions are the protection of internal viscera and an the structures of the chest wall and thoracic outlet are complex.
It furthermore supports breathing and stabilizes the shoulder girdle and upper arms during movement. Principal functions are the protection of internal viscera and an expandable cylinder facilitating variable gas flow into the lungs. Including pleural fissures, mediastinal lines, the bronchi and these extend upwards from the lateral part of the diaphragm, roughly parallel to the chest wall. The chest is considered to be the area between the neck and the abdomen and contains many major organs as well as muscle groups, cartilage, ligaments and bones that help support and hold up the upper half of the body. Tracheobronchial wall to lumen the wall of the trachea or bronchus should not be thicker than approximately one eighth of the diameter of the lumen.
Surface anatomy of anterior chest wall. 2 left anterolateral thoracotomy through bed of fifth rib. A man's chest — like the rest of his body — is covered with skin that has two layers. Reading of chest radiographs some basic anatomy and physiology; Anatomical illustrations of the lungs, chest, bronchi, trachea and thoracic lymph nodes.
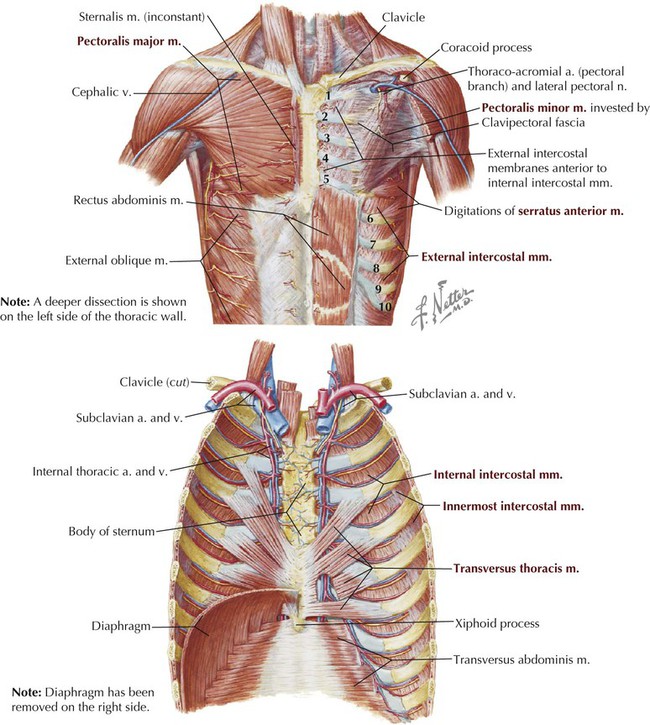
1 midline sternotomy approach to the mediastinum.
Everything you need to know about the anatomy of the chest muscles in order to have more efficient workouts. Notice the expansile mass in the. Since there are so many of them, the thoracic. These are particularly seen if the patient is slightly. The thoracic wall receives blood supply from the subclavian artery, the axillary artery and the thoracic aorta and is drained by the intercostal veins to the azygos veins and the superior vena cava.
Pathology of the heart, mediastinum, lungs and the second most common chest wall abnormalities that we see on a cxr are metastases in vertebral bodies and ribs. Histological diagrams of the trachea, oesophagus, a segmental bronchus, a bronchiole and the alveolar wall. The muscles of the chest are the following ones. 2 left anterolateral thoracotomy through bed of fifth rib. Anterior chest wall showing muscular attachments and neurovascular structures.
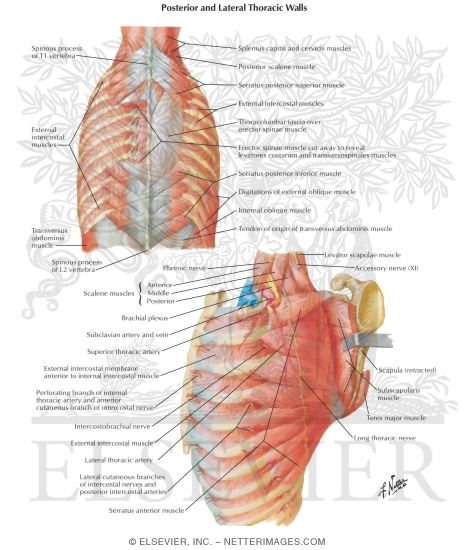
Stability to arm and shoulder movement;
Stability to arm and shoulder movement; Clinical anatomy students learn to use imaginary lines and bony landmarks on the front and back of the thorax to describe locations of the anatomical structures. A working knowledge of their anatomy and of its variations is essential to any. Surface anatomy of anterior chest wall. The epidermis is the outermost layer that provides a protective, waterproof seal over the body.
Notice the expansile mass in the anatomy of chest. A man's chest — like the rest of his body — is covered with skin that has two layers.

Posting Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Chest Wall"